Ultrasound Scan Centre in Bangalore
Fetal Echo Scan Center in Bangalore
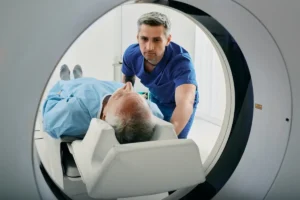
Diagnostic Radiology:
Interventional Radiology:
The various subspecialties of radiology, specific to the areas of the body are:
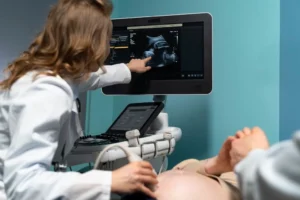
USG
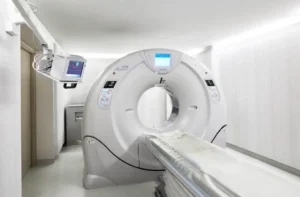
CT SCAN
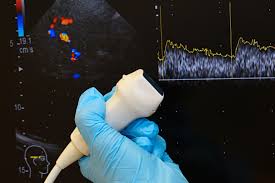
DOPPLER
Doppler ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that deploys sound waves to visualize blood flow, using the Dopplers theory, which allows the assessment of blood flow in various parts of the body, including arteries and veins, and identify potential problems like blockages or narrowed blood vessels. Thus, Doppler ultrasound can be used in situations, including checking blood flow in pregnancy, diagnosing deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and assessment of blood flow to organs.
FETAL ECHO
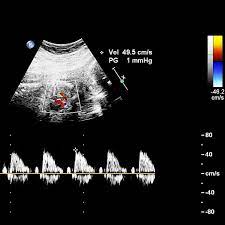
2D ECHO
2D echoes for several reasons:
- Diagnosing heart conditions:
Assessment of abnormalities like valve disorders, heart failure, congenital heart defects, and other structural problems.
- Monitoring heart health:
It can be used to monitor the progression of existing conditions of the heart or the effectiveness of treatments administered.
- Assessing heart function:
Evaluation of the hearts ability in pumping blood and identify any potential issues with blood flow.
SONOMAMMOGRAM
A sonomammogram, is non-invasive and radiation-free procedure of diagnostic imaging that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the breast tissue. It is used to supplement mammography, when breast tissue is dense. Sonomammography helps in the early detection and diagnosis of breast abnormalities.
OUR SPECIALISTS

Dr. Rajesh Murthy
FRCR(London)
Chairman
